
The Basics of Resistance Welding – A Complete Guide
Resistance welding is a process that joins metals using heat and pressure. It is a swift method predominantly used in manufacturing. Here, we will discuss the basics of resistance welding, which will be a comprehensive guide for professionals.
This type of welding technique plays a pivotal role across various industries, fusing materials with efficiency and precision. The process involves generating heat through electrical resistance and applying force to weld the materials together. This method is highly valued for producing strong, reliable bonds without the need for additional materials such as solders or adhesives.
Resistance welding encompasses a range of techniques, including spot, seam, and projection welding, each serving specific applications from automotive manufacturing to aerospace engineering. The process is renowned for its speed, energy efficiency, and the strong, consistent welds it produces, making it an ideal choice for mass-production scenarios. Manufacturers favor this welding for its ability to join metals without altering their properties, maintaining structural integrity, while also being cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Related Article: How to Weld Galvanized Steel: A Step-by-Step Guide

Related Article: Welding Parameters: Tips for Superior Joint Quality
You may also read: How to Get a Welding Job: Top Strategies for Success
Introduction To Resistance Welding
Imagine joining metal pieces with electricity. Resistance welding makes this happen. It’s a process that uses electric current and pressure to weld metal. This welding method is fast and efficient. It’s great for making strong bonds in metal without using filler materials.
The Essentials Of Resistance Welding
Understanding this welding is simple. Here’s what you need to know:
- Electricity flows through metals, causing them to heat up due to resistance.
- When metals get hot enough, they join together.
- You need the right amount of current and pressure for a strong weld.
- Resistance welding machines come in different types. Some are automatic, while others are manual.
Comparing To Conventional Welding Techniques
Resistance welding is unique. Let’s see how it stands out:
| Feature | Resistance Welding | Conventional Welding |
| Speed | Very Fast | Variable |
| Materials | No fillers needed | Often uses fillers |
| Energy Use | Low | Higher |
| Strength | High uniformity | Depends on technique |
In this welding, machines join metals quickly and neatly. It’s different from traditional methods. This can mean fewer resources used and could lead to lower costs.
Key Components And Equipment
When talking about resistance welding, it’s essential to understand the key components and equipment. This process fuses materials with heat generated by resistance to an electrical current. Here’s an insight into the essential tools and elements that make up this welding systems.
Welding Electrodes And Materials
Electrodes are the heart of resistance welding. They apply pressure and conduct electricity to join materials. Copper alloys are common due to their conductivity and strength.
- Spot welding electrodes – Come in various shapes for different applications.
- Seam welding wheels – Roll over materials to create continuous welds.
- Cap electrodes – Designed for spot or projection welding tasks.
Electrode lifespan depends on material and welding conditions. It’s critical to choose the right type for specific tasks.
Power Supplies And Control Systems
Power supplies and control systems manage the welding process. They determine the welding current and cycle times. Two main types exist:
| Type | Feature |
| AC Welding | Standard for many applications; cost-effective. |
| DC Welding | Offers more control; used in high-precision tasks. |
Modern control systems feature microprocessors or PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). They ensure welds meet quality standards. These systems monitor and adjust welding parameters in real time.
Related Article: How Do Auto-Darkening Welding Helmets Work? – A Complete Guide

Related Article: The Ultimate Welding Tools for Beginners
Resistance Welding Processes
This welding uses heat from an electric current to join materials. It’s quick and does not need other metals to work. Think of it like special glue that sticks metals together using heat. Let’s learn about the different ways we can use this awesome method.
Spot Welding Basics
Spot welding is a type of resistance welding. It’s like using a stapler on paper, but for metal. Small spots weld pieces together.
- Press two metal sheets together
- Electric current makes a spot hot
- The spot melts and joins the sheets
It’s perfect for building cars and airplanes because it’s fast and neat.
Seam And Projection Welding
- Seam Welding: Think of drawing a dotted line with a pencil, but with welding. Wheels roll over metal, making a leak-proof seam.
- Projection Welding: Imagine tiny bumps on one metal piece. When pressed against another piece, just the bumps weld. This method is super precise!
This type of welding is great for making tubes, tanks, and even some electrical parts!
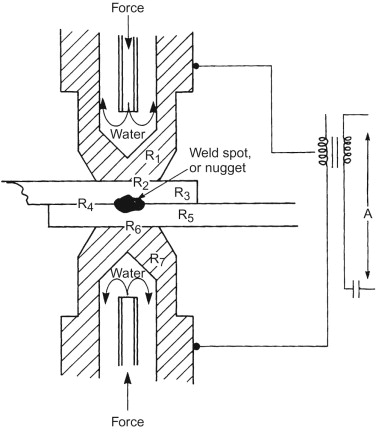
Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Applications Of Resistance Welding
This welding is a marvel in manufacturing, merging metals with precision and strength. This process sees wide use across varied industries, shaped by its reliability and efficiency. From cars to spacecraft, this welding seals the deal. Let’s explore how several sectors harness this technology for their demands.
Automotive Industry Use-cases
The automotive sector relies heavily on resistance welding. Here, every weld ensures safety and durability.
- Car frames: Spot welding gives strength to car skeletons.
- Seat assembly: Welds secure seats for a comfortable ride.
- Mufflers and radiators: Seams are sealed to perfection.
Automatic welding robots achieve consistency in production. They work tirelessly, making sure every join is faultless.
Aerospace And Electronics Applications
In aerospace and electronics, precision is non-negotiable. Resistance welding fits the bill.
| Component | Use-Case |
| Jet engines | Parts endure extreme conditions. |
| Electronic gadgets | Small, secure joins on circuit boards. |
Moreover, the precision in this sector ensures functionality and safety at unbelievable altitudes and in pocket-sized devices.
Related Article: The Ultimate Checklist for Welding Safety Equipment
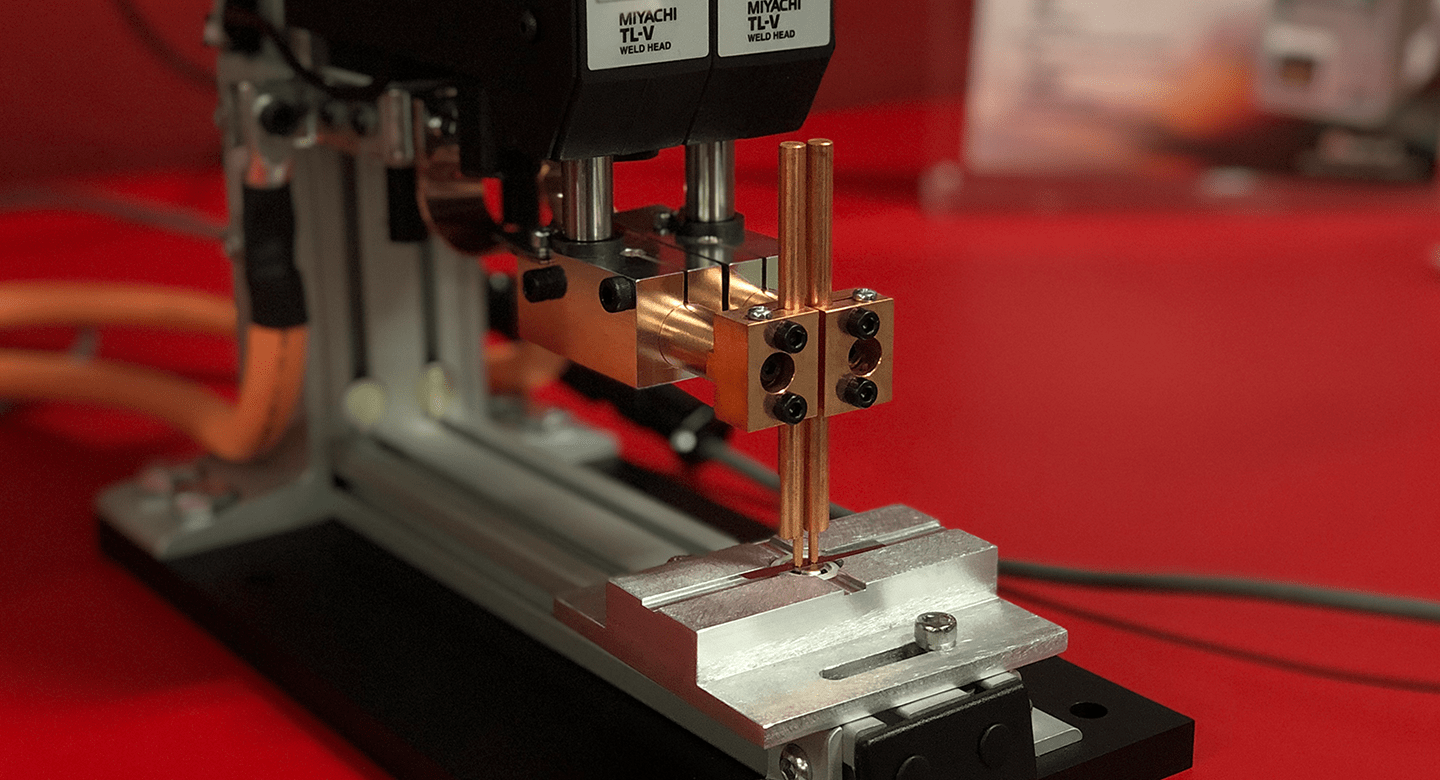
Credit: amadaweldtech.com
Related Article: The Major Welding Defects You Should Know
Challenges And Solutions In Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a robust method used across industries to join metal pieces. Despite its widespread application, professionals face unique challenges with this process.
Common Defects Encountered
Common issues in this welding include:
- Inconsistent welds: Factors like electrode degradation can affect quality.
- Weak welds: Incorrect settings lead to insufficient heat generation.
- Excessive electrode wear: Over time, this can alter weld consistency.
These defects compromise the strength and integrity of the weld, necessitating advanced solutions to ensure reliability.
Advancements In Quality Control
New technologies in resistance welding help overcome these challenges:
| Technology | Benefit |
| Process Monitoring Systems | Real-time data tracking ensures consistent quality. |
| Adaptive Control | Automatic adjustments maintain optimal welding conditions. |
| Electrode Management | Extends electrode life and uniform welds. |
Adopting these measures improves weld strength and reduces waste, supporting high-quality manufacturing standards.
Related Article: How To Choose A Welder: Expert Tips for Perfect Joining
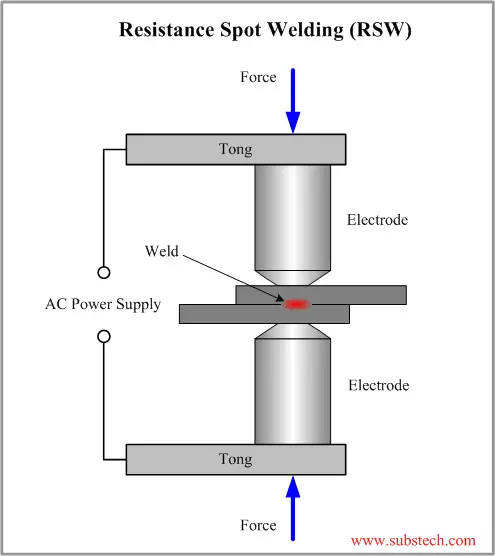
Credit: www.substech.com
Related Article: Top 20 Best Welding Tools of 2025 for Professional Welders
Frequently Asked Questions Of Resistance Welding
What Is Resistance Welding?
This is a process where heat generated from electrical resistance between metal surfaces is used to weld them together. The technique applies pressure and current through the metal pieces, causing them to fuse seamlessly.
Does Resistance Welding Require Filler Material?
No, this welding typically does not require any filler material. The metals are joined by heat produced from electrical resistance, melting the workpieces directly.
What Metals Are Suitable For Resistance Welding?
This welding works well with numerous metals, especially with steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. It is also effective for welding nickel, titanium, and other conductive materials.
How Does this Welding Compare To Arc Welding?
Resistance welding differs from arc welding by not use an arc or filler material. It’s a faster process with less distortion, ideal for mass production and thin materials.
To know more about the Resistance welding Process>>
Conclusion
Resistance welding stands as a robust method for joining metals, marked by efficiency and reliability. Its diverse applications across various industries underscore its importance and versatility. Embracing this technique can lead to stronger bonds and smoother production flows. Let’s harness the power of resistance welding to build a future that’s both structurally sound and technologically advanced.
Related Article: Top 9 Best Welding Helmets of 2025 for Welding Safely
Related Article: Is Welding Hard? – The Ultimate Guide to Know about Welding





One Comment
Pingback: